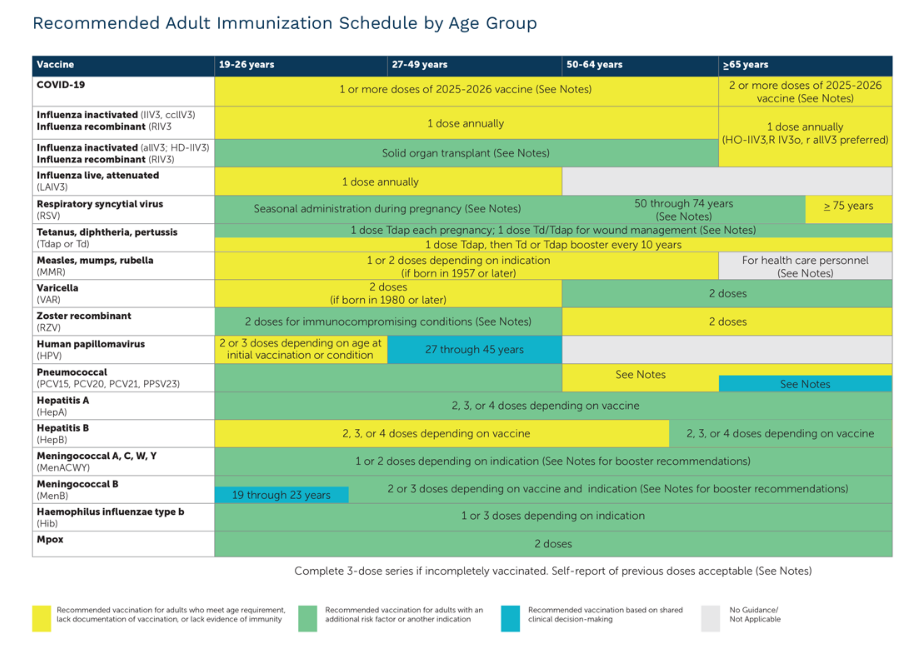
- COVID-19 vaccine: Adults aged 18 – 64 years at higher risk for severe disease should receive least 1 dose of the updated COVID 19 vaccine. All adults 65 years and older should receive at least one dose of the updated COVID-19 vaccines as indicated above.
- Seasonal flu (influenza) vaccine: Adults should get 1 dose every year, especially in the fall, to reduce the risk of getting the flu.
- RSV (respiratory syncytial virus) vaccine: 1 dose protects adults against the severe complications of respiratory syncytial virus.
- People ages 75 and older are recommended to receive 1 dose.
- Adults 50-74 years of age at risk of severe RSV disease are recommended to receive a single dose of RSV vaccine. They should consult with their provider for more information.
- Pneumococcal vaccines: Adults 19-49 years of age with certain underlying medical conditions or other risk factors, 1 -2 doses are recommended.
- Hepatitis B vaccine: This 2 - 4 dose series is recommended for persons 60 years and older with known risk factors such as chronic liver disease.
Additional doses may be recommended for people with chronic conditions based on risk factors after consulting with your provider.
- Meningococcal vaccine: May be recommended for adults with chronic conditions. They should consult with their doctor to see if additional doses are needed.
Individuals should talk with their doctor or other healthcare professional at their next medical appointment to find out which vaccines are recommended.